Full HTTP/3 Protocol Support
NullPrivate now fully supports the HTTP/3 protocol, delivering faster and more secure network experiences for all users
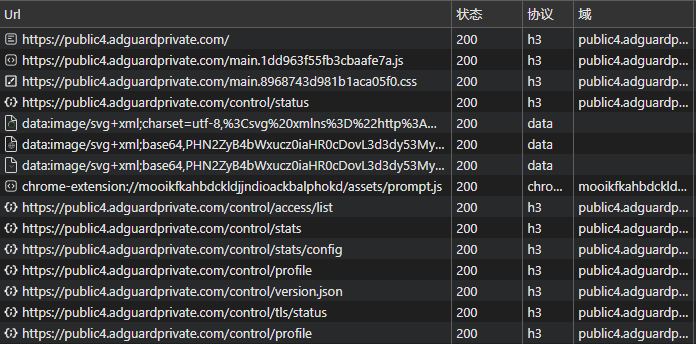
NullPrivate now fully supports the HTTP/3 protocol. All existing users will be automatically upgraded to enjoy the performance gains of HTTP/3 without any additional configuration.
Key Update Notes
- iOS users: Can now use HTTP/3 directly via the DoH protocol, enjoying lower network latency
- Android users: Due to system limitations, still use the DoT protocol for now; support will arrive once Google releases a subsequent version
- Performance boost: First-response times are significantly faster compared to HTTP/2, and connections are established more quickly
- Smart fallback: In environments that do not support HTTP/3, the system automatically falls back to HTTP/2 to ensure service stability
Deep Dive into HTTP/3 Technology
HTTP/3, the latest version of the HTTP protocol, is built on Google’s QUIC transport protocol and brings several revolutionary technical advantages:
Core Features
QUIC protocol over UDP
- Dramatically reduces connection-establishment time
- Improved multiplexing capabilities
- Smarter packet-loss handling
Optimized performance
- Zero-round-trip-time (0-RTT) handshakes
- Enhanced congestion control
- Connection-migration support
Enhanced security
- Integrated TLS 1.3
- Encrypted handshake process
- Reduced risk of man-in-the-middle attacks
Connection-Establishment Comparison
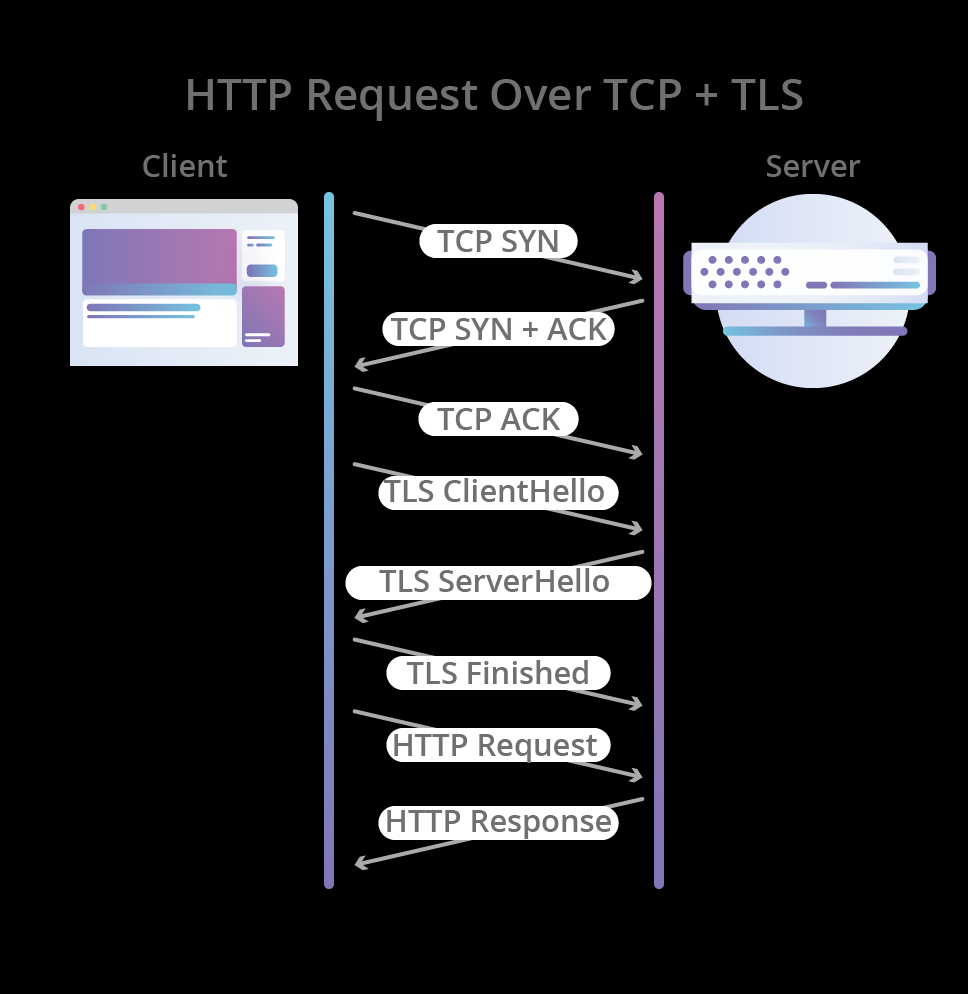
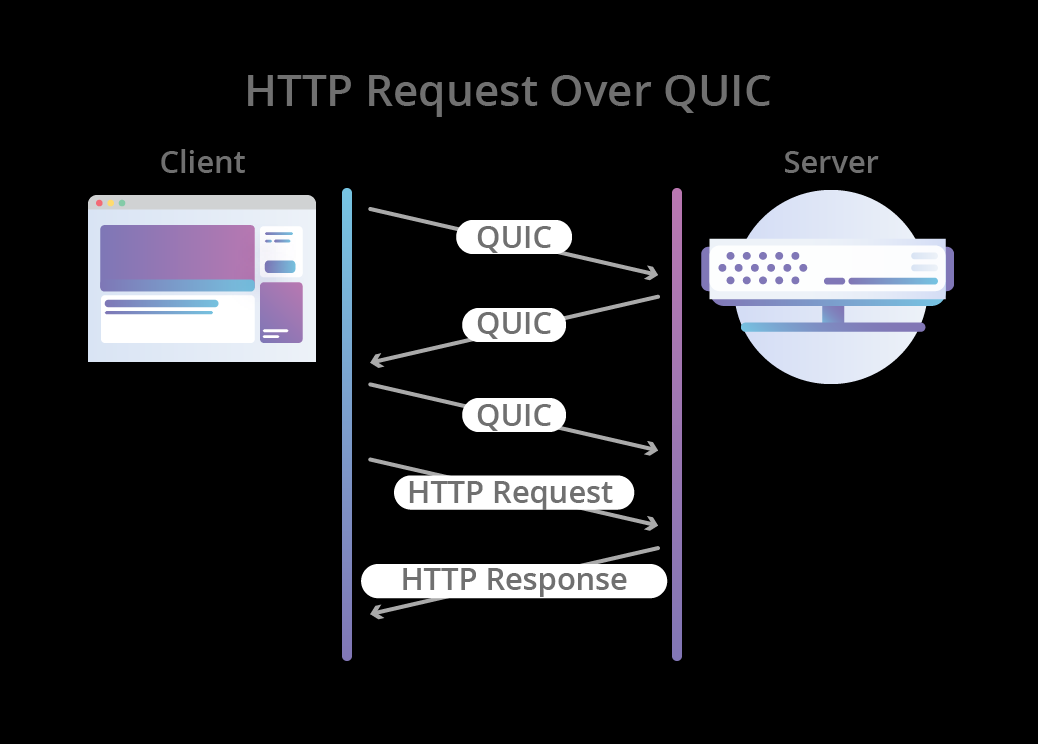
Usage Recommendations
- Ensure your client supports the HTTP/3 protocol
- Keep your client up to date
- When network conditions are restricted, the system will automatically fall back to HTTP/2
Important Notes
- In some regions, networks may restrict UDP traffic, affecting HTTP/3 performance
- Performance may vary across different network environments
- The system will automatically select the optimal protocol based on network conditions